Data Visualization: Gestalt Principles of Design
In the world of design, understanding how humans perceive visual elements is crucial. One of the fundamental theories that designers rely on is Gestalt psychology. Gestalt principles explain how our minds organize visual information into meaningful patterns and wholes. These principles play a vital role in various design disciplines, including graphic design, web design, and architecture. In this post, we’ll explore six key Gestalt principles: proximity, continuity, closure, enclosure, similarity, and connection.
Proximity
Proximity refers to the principle that elements placed close together are perceived as belonging to the same group. When objects are near each other, we tend to see them as related or connected in some way. In design, grouping related elements together through proximity helps create organization and hierarchy. For example, in a website layout, grouping navigation links close to each other signals to users that they are related and serve a similar function.

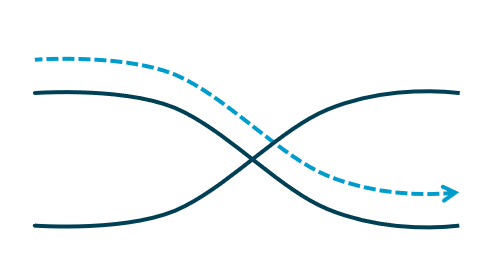
Continuity
Continuity involves the tendency to perceive continuous lines or patterns even when they are interrupted. Our minds naturally seek patterns and flow, so we perceive elements that align or flow smoothly as belonging together. In design, continuity helps guide the viewer’s eye and creates a sense of unity. For instance, a series of images aligned in a straight line creates a visual flow that leads the viewer’s gaze from one image to the next.
Closure
Closure refers to the principle that our minds tend to fill in missing information to perceive incomplete shapes or forms as whole. Even when parts of an image are missing or obscured, our brains automatically complete the missing parts to form a recognizable whole. Designers often leverage this principle to create minimalist or abstract designs that encourage viewers to actively engage with the content by mentally completing the missing elements.
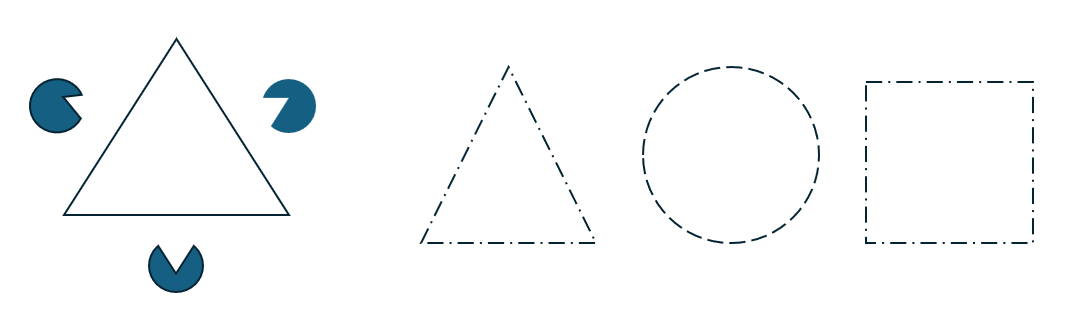
Enclosure
Enclosure involves the perception of elements enclosed within a boundary as a single unit. When elements are surrounded by a common border or shape, we perceive them as belonging together. Designers use enclosure to group related content and create visual emphasis. For example, placing text within a colored box or a border draws attention to that content and distinguishes it from surrounding elements.
Similarity
Similarity refers to the principle that elements with similar attributes, such as shape, size, color, or texture, are perceived as belonging to the same group. When elements share common characteristics, we automatically group them together. Designers use similarity to create visual harmony and convey relationships between elements. For instance, using consistent colors or fonts across related sections of a design helps reinforce their connection.
Connection
Connection involves the perception of elements arranged in a way that suggests a relationship or continuation. Even when elements are physically separate, our minds perceive them as connected if they are aligned or oriented in a cohesive manner. Designers use connection to establish visual relationships between disparate elements and guide the viewer’s eye through the design. For example, aligning text with accompanying images creates a visual connection that enhances comprehension and flow.
In conclusion, Gestalt principles provide valuable insights into how humans perceive and interpret visual information. By understanding these principles, designers can create more effective and engaging designs that resonate with their audience. Whether designing a website, a logo, or an architectural space, incorporating Gestalt principles can elevate the impact and clarity of the design. By harnessing the power of proximity, continuity, closure, enclosure, similarity, and connection, designers can craft visual experiences that captivate and communicate with precision.
Check out our easy-to-read one pager on this subject. (Download here)